|
|
| This glossary uses network terms from the OSI model. Click on one of the categories on the left or on the image below. Click the View All link to see all terms. Use the alphabet to jump to that letter. Some of the terms could be used on multiple layers, but they are grouped in the most common layer. |
Application
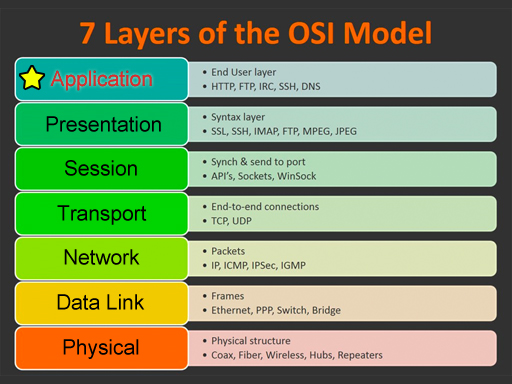
View All
|
|
|
#
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
|
C
CLI (Command Line Interface)† |
| A user interface (UI) characterized by a text-based individual command parser. Most modern operating systems have a CLI; for some operating systems, the CLI is the primary interface. The most common accompaniment to the CLI is the graphical user interface (GUI), with which a mouse or other pointing device is often used. (Application Layer) Top |
|
|
D
DNS (Domain Name System)† |
| A TCP/IP protocol and general term for the global or enterprise network of systems responsible for resolving fully-qualified domain names (FQDNs) to IP addresses. A domain name is a structured identifier for the zone that contains related devices or devices under a common administration. (Application Layer) Top |
|
|
F
FTP |
| Stands for "File Transfer Protocol." FTP is a protocol designed for transferring files over the Internet. Files stored on an FTP server can be accessed using an FTP client, such as a web browser, FTP software program, or a command line interface. (Application Layer) Top |
|
|
G
GUI (Graphical User Interface)† |
| A computing user interface (UI) characterized by a full-screen work area and icons that represent objects such as folders and files. GUIs work well with pointing-style input devicesómice and trackballs, for instanceóbecause the work area is laid out as a two-dimensional Cartesian grid. (Application Layer) Top |
|
|
H
HTTP |
| Stands for "Hypertext Transfer Protocol." HTTP is the protocol used to transfer data over the web. It is part of the Internet protocol suite and defines commands and services used for transmitting webpage data. (Application Layer) Top |
|
|
I
IRC |
| Stands for "Internet Relay Chat." IRC is a service that allows people to chat with each other online. It operates on a client/server model where individuals use a client program to connect to an IRC server. Popular IRC clients include mIRC for Windows and Textual for OS X. Several web-based clients are also available, including KiwiIRC and Mibbit. (Application Layer) Top |
|
|
P
Proxy server† |
| An edge device that acts on behalf of other devices. Proxy servers provide multiple functions and are generally positioned in such a way that all outbound traffic must pass through the server. This positioning supports most of the serverís roles, such as permitting or denying different types of outbound traffic generated by clients within the intranet and caching received web content as clients request it. (Application Layer) Top |
|
|
S
SSH |
| Secure Shell (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Typical applications include remote command-line, login, and remote command execution, but any network service can be secured with SSH. (Application Layer) Top |
|
|