|
|
| This glossary uses network terms from the OSI model. Click on one of the categories on the left or on the image below. Click the View All link to see all terms. Use the alphabet to jump to that letter. Some of the terms could be used on multiple layers, but they are grouped in the most common layer. |
Presentation
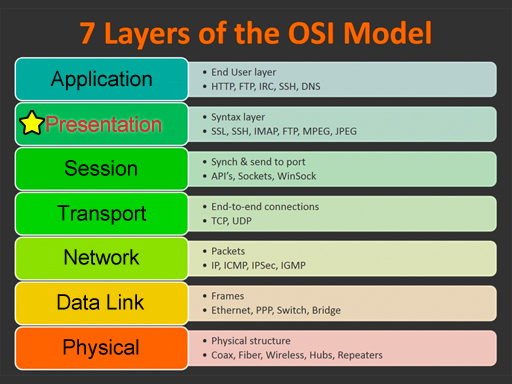
View All
|
|
|
#
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
|
A
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) |
| The character set used in the Disk Operating System (DOS) of the original IBM Personal Computer (IBM/PC) line. A character set is a code that assigns one of the binary permutations in the character set to each of the characters available to text-based applications running on the operating system. ASCII is a 7-bit code while Extended ASCII is an 8-bit code. The result is a set of 128 characters and 256 characters, respectively. (Presentation Layer) Top |
|
|
C
Compression |
| The reduction of the amount of data that is transmitted or stored. Some compression algorithms build a dictionary of longer codes that have been replaced by shorter codes before transmission or storage. The receiving device or the retrieving application uses the dictionary to expand the compressed information into its original form. This is known as lossless compression. Lossless compression is ideal for absolute data, such as financial information in a spreadsheet that must not be misinterpreted. (Presentation Layer) Top |
|
|
Console |
| The input and output devices employed by the user in operating a user interface (UI). Commonly, a terminal is the combination of a keyboard, a mouse (optionally), and a monitor. Consoles allow users to interface with systems, such as computers, routers, and switches, to configure or control them. The term “console type” is often used to refer to the terminal type, such as VT-100, set in terminal emulation software—Putty, for instance—to match similar settings on the device being managed by the console. Devices called keyboard, video, mouse (KVM) switches can be used to switch among multiple systems, controlled one at a time by a single console. (Presentation Layer) Top |
|
|
E
Encryption |
| The act of altering data to make it unreadable by any person or device, except by the intended recipient, with which a security association has been negotiated, or by an authorized retrieving application. From the perspective of data security, encryption is the primary mechanism for providing confidentiality in stored or transmitted data. (Presentation Layer) Top |
|
|
I
IMAP |
| In computing, the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) is an Internet standard protocol used by email clients to retrieve email messages from a mail server over a TCP/IP connection. IMAP is defined by RFC 3501. (Presentation Layer) Top |
|
|
J
JPEG |
| Stands for "Joint Photographic Experts Group." JPEG is a popular image file format. It is commonly used by digital cameras to store photos since it supports 224 or 16,777,216 colors. The format also supports varying levels of compression, which makes it ideal for web graphics. (Presentation Layer) Top |
|
|
L
Load balancing |
| Sending proportionate data traffic across multiple signal pathways. The term load balancing is often used interchangeably with load sharing. However, load sharing can technically be achieved simply by using multiple pathways to send data in the same general direction, but load balancing seeks to adjust shared loads based on a criterion, up to and including maximizing throughput per pathway. (Presentation Layer) Top |
|
|
M
MPEG |
| Stands for "Moving Picture Experts Group." MPEG is an organization that develops standards for encoding digital audio and video. It works with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) to ensure media compression standards are widely adopted and universally available. (Presentation Layer) Top |
|
|
S
Single Sign-On (SSO) |
| An authentication model in which only one set of login credentials is required to gain access to many systems. (Presentation Layer) Top |
|
|
Spooling |
| Storing content to be printed in a buffer held in RAM or on a drive until the printer is ready to process the print job. Print spoolers can exist in the printer, in the server to which the printer is attached, and in the host that originally generated the print job. Using a spooler allows the host to continue with other processing while the printer becomes ready to receive the print job. (Presentation Layer) Top |
|
|